How To Turn Off Engine Power Reduced Chevy Malibu
In general, the “Engine Power Reduced” warning in your Chevy Malibu acts like a fail-safe device that is triggered when the system of the car detects that something is wrong with the performance of the engine.
This usually cuts down acceleration and overall power in order not to create further critical damage. Possible causes include a faulty throttle body, malfunctioning sensors, wiring issues, or problems with the engine control module.
Disable the warning by diagnosing the problem with an OBD-II scanner, repairing said problem, and then resetting the system.
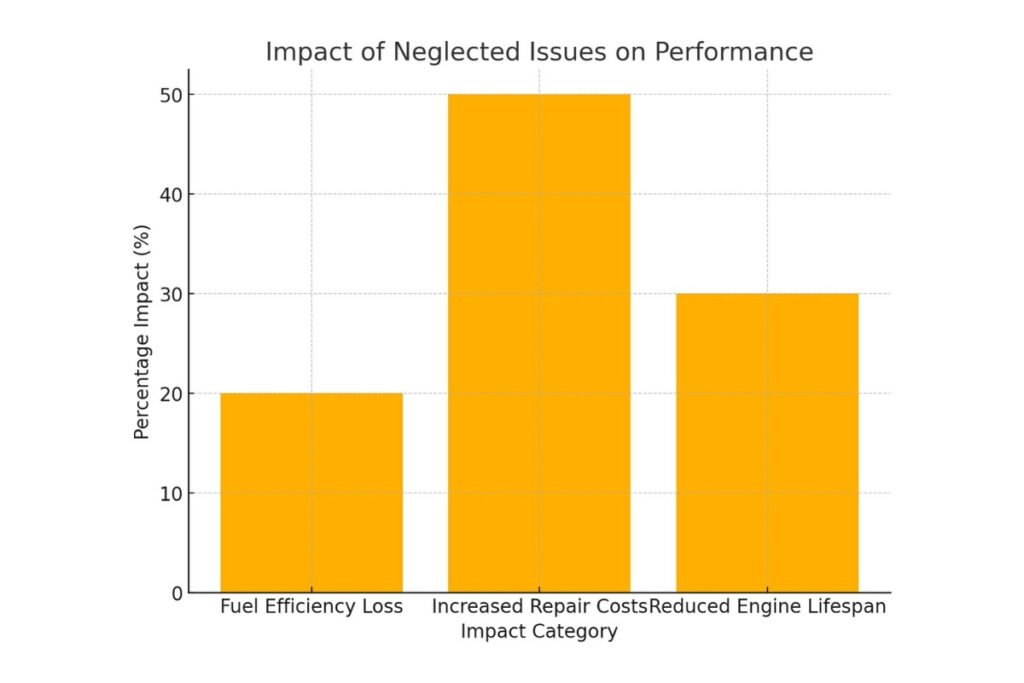
What Does Reduced Engine Power Chevy Mean?
The “Reduced Engine Power” warning light indicates that the onboard computer in your Chevy vehicle, such as a Chevy Malibu, has detected something that it doesn’t like about the performance of the engine.
If this warning is turned on, then the performance of the vehicle has been intentionally limited to prevent damage to major components.
Common Symptoms of Engine Power Is Reduced Chevy:
- Severe loss of acceleration: It can be very slow and not able to reach high speeds.
- Check Engine Light on: Sometimes appears together with the “Reduced Engine Power” warning.
- Limp mode engages: The car will limit the function of the engine so that safe operation can be achieved until repairs are made.
- Throttle not responding: Throttle pedal may be pressed but speed does not increase as should.
Diagnostic Error Codes and Their Meanings
| Error Code | Description | Possible Fix |
|---|---|---|
| P2135 | Throttle/pedal position sensor switch issue | Replace the sensor or throttle body |
| P2101 | Throttle actuator control motor circuit range | Inspect throttle actuator wiring |
| P1516 | Throttle actuator control module performance | Replace the throttle control module |
| P0121 | Throttle/pedal position sensor performance issue | Calibrate or replace the sensor |
Top 10 Serious Causes of Engine Power Reduced in a Chevy Malibu
The “Engine Power Reduced” warning in a Chevy Malibu is a protective mode engaged by the vehicle’s computer whenever it feels there is an impending problem that could lead to engine damage or degraded performance.
While it does protect the engine, it can severely reduce acceleration and overall driving capability. A thorough understanding of what actually causes this warning will provide a clear view for diagnosis and timely resolution.
Most of the problems originate from critical parts like the throttle body, sensors, or even fuel delivery systems. If these are left unattended, the consequences may be very expensive repairs, poor fuel economy, or a total failure of the engine.
The following is a detailed look at the top 10 causes originating from this warning and how to fix them accordingly:
Throttle Body Malfunction:
The throttle body controls the amount of air entering into the engine. A dirty, clogged, or faulty throttle body restricts airflow, resulting in poor acceleration and reduced engine performance.
Cleaning or replacement of the throttle body resolves the issue.
Faulty Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor:
It monitors the gas pedal for how much it is depressed and sends signals to the ECM. In case of failure, the ECM reduces the power of the engine to save the engine from getting damaged.
Replacing the faulty sensor will solve the problem.
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) failure:
The throttle position sensor monitors the position of the throttle body and relays important information to the ECM. A faulty TPS causes disrupted operation of the engine, leading to unreliable acceleration and loss of power.
Replacing the TPS will restore normalcy.
ECM issues:
The ECM governs the overall performance of the engine. Any hardware failure or software error in the ECM can mismanage the functions of the engine, which in turn can trigger reduced power mode. T
his is usually resolved by reprogramming or replacing the ECM.
Damaged or Corroded Wiring:
Wiring connects sensors, the throttle body, and the ECM. When wiring is corroded or damaged, it interrupts the communication of information, resulting in reduced power mode.
The solution will be repairing or replacing the damaged wiring.
Clogged Air Filter:
A clogged air filter obstructs the normal flow of air into the engine, hence decreasing efficiency and loss of power. Replacing the air filter ensures normal flow, thus curing the reduced power issue.
Faulty Mass Air Flow Sensor:
Basically measures the air coming inside the engine. This sensor sends data to the ECM. In case it fails, it would send wrong information for incorrect air-fuel mixtures that would give less power.
Cleaning or the replacement of the sensor would solve the problem.
Fuel Delivery Issues:
When the fuel pump fails, fuel injectors block, or fuel lines become clogged, it cuts off the flow of fuel to the engine and causes misfires and loss of power.
After repairing or replacing the concerned fuel system component, the normal operation will be restored.
Faulty Oxygen Sensors:
Oxygen sensors monitor the exhaust gases and adjust the air-fuel mixture. Bad sensors give false readings, which leads to poor engine performance and thus reduces power mode.
Replacing the oxygen sensors resolves this problem.
Catalytic Converter Issues:
A clogged or damaged catalytic converter restricts the flow of exhaust and increases back pressure, which cuts down on power.
The repair or replacement of the catalytic converter restores performance.
| Cause | Description | Solution | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throttle Body Malfunction | Clogged or dirty throttle body | Clean or replace | $250 – $600 |
| Accelerator Pedal Sensor Fault | Fails to relay gas pedal position | Replace the sensor | $100 – $300 |
| Wiring Issues | Corroded or disconnected wires | Repair or replace wiring | $100 – $500 |
| ECM Failure | Malfunctioning engine control module | Reprogram or replace | $400 – $1,200 |
How To Turn Off Engine Power Reduced Chevy Malibu
In simple terms, this “Engine Power Reduced” warning is a way that Chevy vehicles-like the Malibu-are programmed to prevent further engine damage. This mode restrains the performance of the car, preventing catastrophic failures while alerting the driver about an underlying problem.
While this light can be infuriating, it’s important to take it seriously for the safety and performance of your vehicle in the long run. The following steps will walk you through troubleshooting and temporarily fixing the problem.
Remember, these steps are not permanent repairs; finding and correcting the root cause is essential for long-term reliability.
Step 1.
Safely turn off the engine and stop your vehicle. Pull on to a safe location if possible, especially if one feels a severe drop in power and responsiveness.
Turning off of the engine allows no further damages while trying to diagnose the problem.
Step 2.
Observe any apparent problems under the hood. Pop open the hood and see if there is any apparent issue, like a disconnected wiring, loose throttle body, or debris on the sensors.
Sometimes, solving these minor issues will clear the warning.
Step 3.
Restart the vehicle for a basic reset. That means turning the ignition off, waiting for about 10 seconds, and restarting the car.
This often clears temporary glitches in the ECM, but if the problem is persistent, the warning may reappear.
Step 4.
Employ an OBD-II scanner to read the error codes. Finally, hook up the scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port to indicate the exact error codes regarding the “Engine Power Reduced” warning.
Note down the code and description for understanding the possible causes.
Step 5.
Find the cause or get a professional. Based on the error codes and your technical expertise, clean the throttle body, check the sensors, and tighten loose connections.
If this problem is really complicated, look for a professional mechanic to correct it permanently.
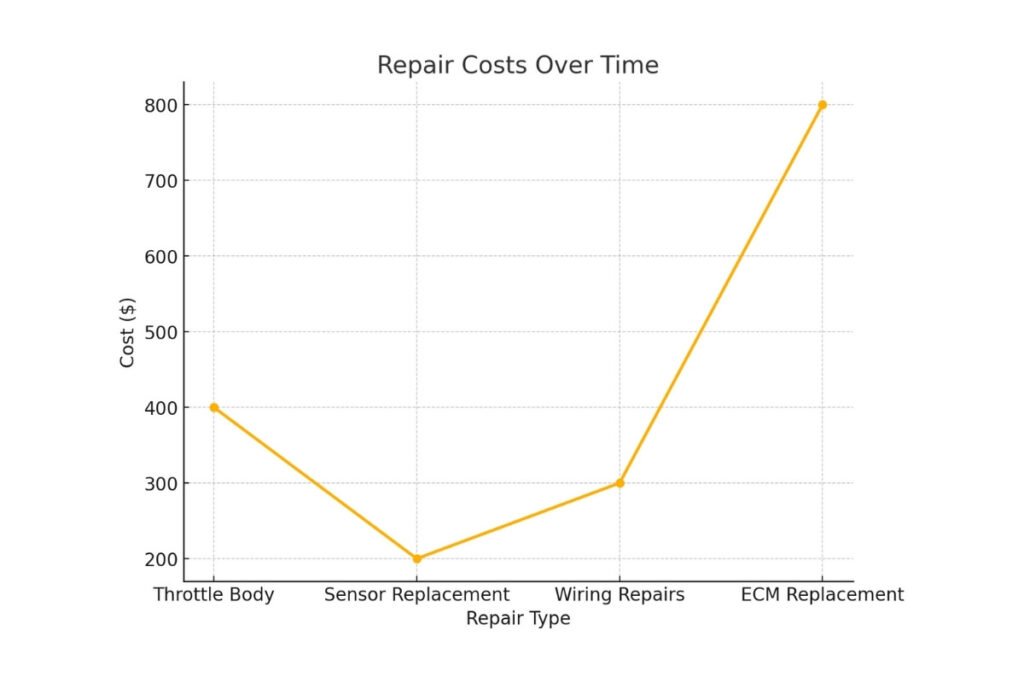
When to Seek Professional Help
While some of the causes that may trigger the “Engine Power Reduced” warning can be diagnosed and fixed at home, there are those situations that would require one to consult the hands of a professional.
When to get a mechanic can save you time and further damage and see the problem dealt with correctly.
Signs the Problem Needs a Mechanic
- Persistent Warning Light: The “Engine Power Reduced” warning, if persistent and failing to turn off after basic troubleshooting or reset, points out that the problem might be serious enough to require advanced diagnostics.
- Complex Error Codes: Some error codes, especially those relating to the engine control module, wiring issues, or multiple components, may suggest problems beyond basic DIY repairs.
- Unusual Symptoms: Frequent stalling, unusual noises, and erratic throttle behavior are symptoms that can suggest deeper mechanical or electrical problems.
- No Improvement after DIY Repairs: If you have cleaned or replaced parts like the throttle body or sensors and the warning persists, a mechanic’s expertise is required.
- Specialized Tools Required: Some of these issues, such as reprogramming the ECM or diagnosing complex electrical faults, require specialized equipment and expertise.
- Vehicle Safety Concerns: If the car exhibits severe performance problems, such as extreme loss of power or inability to accelerate properly, it is safer to let a professional take a closer look at it.
Average Costs for Common Repairs Causing “Engine Power Reduced”
- Throttle Body Replacement: $250 – $600 (parts and labor)
- Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Replacement: $100 – $300
- Throttle Position Sensor Replacement: $150 – $400
- Engine Control Module (ECM) Repair or Replacement: $400 – $1,200
- Wiring or Electrical Repairs: $100 – $500 (depending on the extent of the repair)
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Replacement: $200 – $400
- Catalytic Converter Replacement: $900 – $2,500
- Oxygen Sensor Replacement: $150 – $300 per sensor
- Fuel System Repairs (e.g., fuel pump or injectors): $300 – $1,000
- Professional Diagnostics: $100 – $150 for scanning and finding out what is wrong
Why Professional Help Counts
Professional mechanics have the right tools, experience, and knowledge to correctly diagnose and fix the root cause of the “Engine Power Reduced” warning.
This will ensure that the problem is fixed right and further complications are avoided, saving you money and stress in the long run.
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
| Component | Frequency | Action | Estimated Cost |
| Throttle Body | Every 30,000 miles | Clean to prevent clogging | $50 – $100 |
| Air Filter | Every 15,000 miles | Replace | $20 – $50 |
| OBD-II Diagnostics | Yearly or as needed | Scan for error codes | $100 per scan |
FAQs
What does “Engine Power Reduced” Mean on a Chevy Malibu?
This warning light means that an onboard computer is detecting a trouble code that affects your engine performance or power, automatically reducing the power to help protect the engine.
Can I Drive My Chevy Malibu with the “Engine Power Reduced” Warning?
Although the car may still be driven, it is highly inadvisable to drive on under such a warning since something would be wrong somewhere that will critically lower safety or cause further damage.
What Causes “Engine Power Reduced” Warning on a Chevy Malibu?
General causes include everything from a bad throttle body or faulty sensors, such as accelerator pedal position sensors or throttle position sensors, to wiring issues down to problems stemming from the ECM.
How Do I Fix the “Engine Power Reduced” Issue on My Chevy Malibu?
This requires diagnosis of the particular cause. An OBD-II scanner will be able to provide error codes. Depending on the problem, solutions may involve cleaning or replacing the throttle body, sensors, or even addressing wiring issues.
Is It Expensive to Repair the “Engine Power Reduced” Problem on a Chevy Malibu?
The repair cost depends on what it is. Throttle body replacement costs anywhere from $250 to $600, while sensor replacements may cost between $100 and $400.
Can a Dirty Air Filter Cause the “Engine Power Reduced” Warning?
Yes, a dirty air filter will limit airflow into the engine and might cause the warning because the engine will not be running efficiently.
Will Disconnecting the Battery Reset the “Engine Power Reduced” Warning?
Disconnecting the battery will only delete the warning for a limited time, and if the problem causing it is not solved, it’s most probably going to come back.
How Long Can I Drive with the “Engine Power Reduced” Warning?
Don’t drive while this warning is on. Solve it as soon as possible, or you may run into a real safety problem along with more engine damage.
Can Extreme Weather Cause an “Engine Power Reduced” Warning in a Chevy Malibu to Come On?
Extreme weather will often highlight a problem and make it worse but isn’t usually the actual cause that creates the issue.







